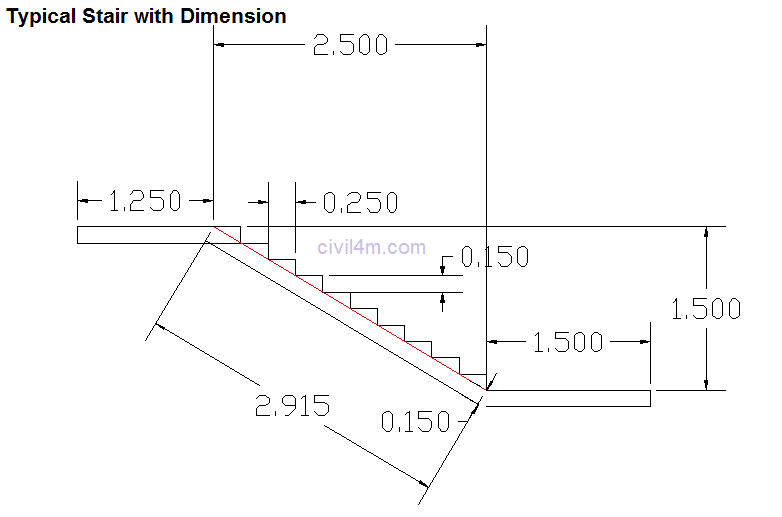
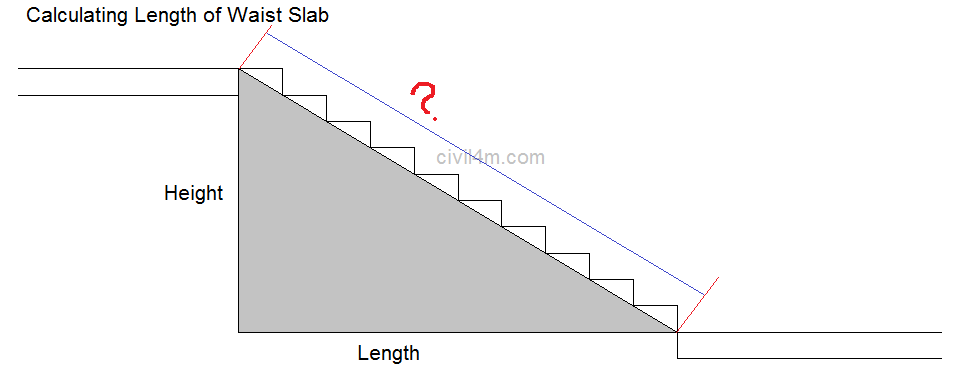
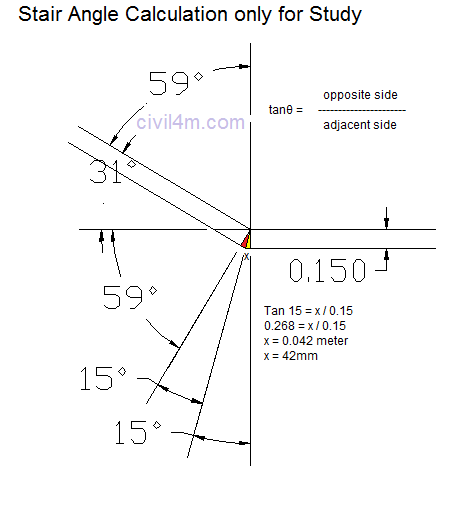
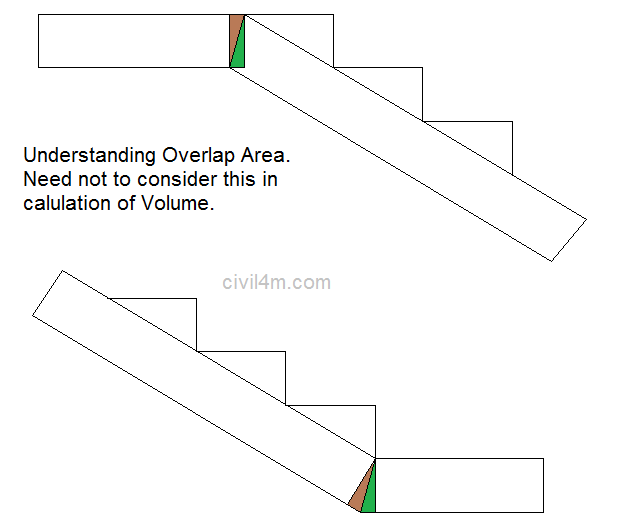
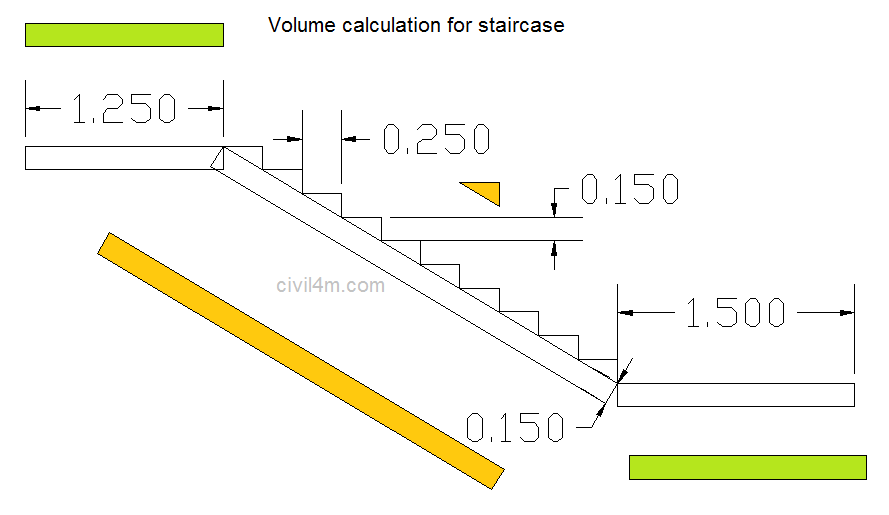
The structures that are constructed across drainages ( natural or artificial ) to retain water to the required height , are known as dams. The dams which are wholly constructed with stones , are called masonry dames
The following forces generally act on a dam section
1- weight of masonry acting downward
2- pressure of water acting horizontal
To avoid tension in masonry , it is ensured that the resultant of the forces on the dam section , lies within the middle third of the section
While analysing dam section , one should always consider a unit length of the dam .
Now consider the trapezoidal dam section of unit length
Let w= density of water retained
h= height of water retained
W = total weight of the masonry acting at its C-G
Water pressure P= 1/2 wh2 acting at h/3 form the base
The resultant R of the force P and W intersect the base at E . To locate E, take the moments of P and W about E. The resultant R may be considered to be equivalent to horizontal through P and vertical force W . The horizontal force does not affect the stresses at the base. The stresses which are developed at the base are, therefore, only due to load W and acts with an eccentricity ,
The maximum stress at the base is at the outer edge away from the water face and minimum stress will be at the edge near the water face